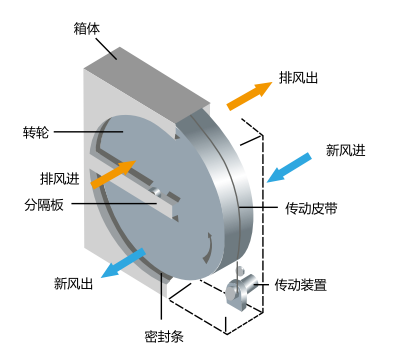
There are two types of rotary energy recovery heat exchangers, namely, full heat type and sensible heat type. The wheel is used as a heat storage core. The fresh air passes through one semicircle of the wheel, while the exhaust air passes through the other semicircle of the wheel in reverse. In this way, the fresh air and the exhaust air pass through the wheel alternately and reversely. In winter, the wheel heat storage core absorbs the heat (humidity) in the exhaust air. When it turns to the fresh air side, the heat storage core will release the heat (humidity) in it due to the temperature (humidity) difference. When it turns to the exhaust side again, it continues to absorb the heat (humidity) in the exhaust air. Such a reciprocating cycle realizes energy recovery, and its working principle is shown in the figure. In the summer cooling operation, it is the opposite process. When the full heat wheel is running, the water molecules in the air will be adsorbed into the molecular sieve coating on the surface of the honeycomb. When it turns to the other side, the water molecules will be released due to the pressure difference of the water molecules. The full heat wheel uses the exhaust air and the incoming fresh air to exchange sensible heat and latent heat to realize energy recovery, thereby achieving energy saving and maintaining good indoor ventilation. In summer, the fresh air can be pre-cooled and dehumidified, and in winter, the fresh air can be pre-heated and humidified.
0 Comments