Netizens who are familiar with the layout of data centers will find that many data centers are located near large reservoirs or water sources. For example, the JD Cloud East China Data Center in Suqian, Jiangsu is less than 2 kilometers away from Luoma Lake. Another example is that there are a large number of data centers near the Guanting Reservoir in Huailai, Hebei. Why are these places chosen? To a large extent, it is because the cooling of data centers requires a lot of water, and being close to water sources is nothing more than the most economical and effective solution. Unlike the cooling methods of many large public buildings such as airports and stations, data center cooling often uses water as a medium to remove the heat generated by the data center through the evaporation of water, such as the chilled water cooling solution and the popular evaporative cooling solution in recent years.
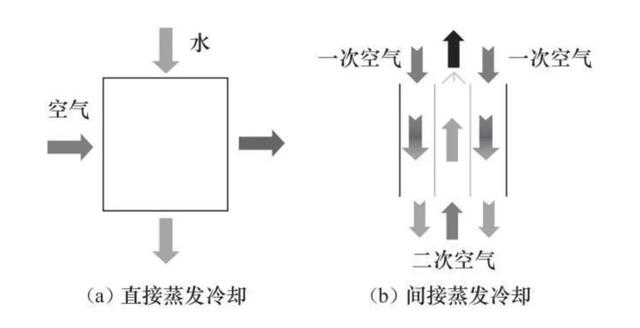
In terms of refrigeration technology, evaporative cooling technology can be divided into direct evaporative cooling technology and indirect evaporative cooling technology. In direct evaporative cooling, water is sprayed directly into unsaturated wet air. However, due to the direct contact between air and water, its moisture content increases, so there are certain application limitations. In indirect evaporative cooling, the working medium first passes through the indirect evaporative cooler to form a wet channel, and the output medium flows through the dry side channel. The wet side medium absorbs the heat of the dry medium and evaporates with the help of the wet surface, thereby cooling the output medium. Since the working medium is not in direct contact with water, its moisture content remains unchanged, and the air is cooled by isohumidity. This is the advantage of indirect evaporative cooling technology. With water and air as cooling media, indirect evaporative cooling technology uses air-to-air indirect heat exchange, so that when the external ambient temperature is low, the heat generated inside the data center can be taken away by low-temperature air (dry mode), and when the external ambient temperature is high, the evaporation of water can be used to help dissipate heat (wet mode). In this way, no matter what the external environment is, the data center can choose a mode that suits it to achieve a good heat dissipation effect; even when the ambient temperature continues to rise, the mixed mode can be turned on to maximize heat dissipation. From this point of view, the advantage of indirect evaporative cooling technology is that it can reduce the temperature of the computer room and greatly increase the time of natural cooling while isolating the indoor and outdoor air. To date, indirect evaporative cooling technology has been widely adopted by the industry. In addition to its advantages in energy saving and emission reduction, it is also superior to traditional solutions in terms of phased deployment, construction cycle, reliability, and TCO. Therefore, it has been widely recognized by the industry. According to statistics, the application of indirect evaporative cooling technology has grown rapidly in the past few years. The annual installed capacity in mainland China has rapidly increased from less than 100 sets in 2017 to more than 1,000 sets in 2021, with a rapid growth momentum.
This also explains why the "Guizhou in the south and Ulanqab in the north" layout of data centers has been formed in recent years. Guizhou is traditionally considered a remote province, but the annual temperature difference here is small due to its altitude advantage. For example, the annual average temperature in Gui'an New District, where data centers are "clustered", is 15°C, and the air quality rate in 2021 reached 97.4%, which is very consistent with the requirements of indirect evaporative cooling for air temperature and quality. In contrast, Ulanqab in Inner Mongolia has a more obvious advantage - the average temperature throughout the year is 2.6°C, and even in the heating season in the north, the air quality can achieve 100%, and it also has the conditions for natural cooling in terms of temperature and quality.

0 Comments